Twice-Yearly Dosing With UPLIZNA
UPLIZNA is the only approved monotherapy for NMOSD with a twice-yearly dosing schedule after 2 initial start-up doses.1

Betsy
Switched to UPLIZNA in 2021.
Individual results may vary. Hear a patient’s
experience with NMOSD-related hospitalization.

Betsy
Switched to UPLIZNA in 2021.
Individual results may vary. Hear a patient’s
experience with NMOSD-related hospitalization.
Reduction in Hospitalizations
*In the RCP.2
Reduction in Worsening Disability
Consider open-label treatment phase study limitations when interpreting results. The OLP was not blinded, not controlled, and included inherent self-selection bias for remaining in the trial. During the OLP, a total of 42 patients (19.4%) discontinued, of which 5 patients (2.3%) discontinued due to adverse events.
†Compared to placebo in the RCP. Data from a post hoc analysis of N-MOmentum conducted by JL Bennett et al.3
‡Includes both AQP4-IgG+ and AQP4-IgG– patients.3
The EDSS analysis included visits during an attack, with EDSS progression driven by the expected increase in EDSS at the time of attack. Therefore, these results should not be interpreted as impacting disability independent of attack reduction. Additionally, subjects were not followed up for the same amount of time, resulting in missing data which may have introduced biases into the analysis. Subjects with missing data are imputed as worsening.
§Worsening disability was assessed by the EDSS at last visit during the RCP, defined as 1) worsening of 2 or more points in EDSS score for subjects with baseline score of 0; 2) worsening of 1 or more points in EDSS score for subjects with baseline score of 1 to 5; 3) or worsening of 0.5 points or more in EDSS score for subjects with baseline score of 5.5 or more.2
‖In the RCP.2
Hear a patient’s story about NMOSD-related disability.
B-Cell Depletion
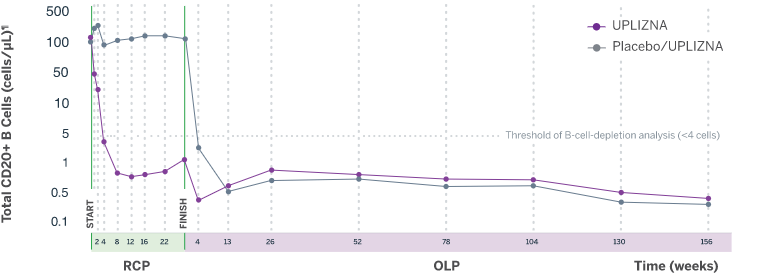

Analysis is exploratory and has not been adjusted for multiple comparisons. No conclusions of statistical or clinical significance can be drawn.
¶For CD19+ B-cell counts, assays for CD20+ B cells are used because the presence of UPLIZNA interferes with CD19+ B-cell assay.2
UPLIZNA is the only approved monotherapy for NMOSD with a twice-yearly dosing schedule after 2 initial start-up doses.1
AQP4-IgG+, aquaporin-4-immunoglobulin G positive; EDSS, Expanded Disability Status Scale; NMOSD, neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder; OLP, open-label period; RCP, randomized controlled period.
INDICATION UPLIZNA (inebilizumab-cdon) is indicated for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) in adult patients who are anti-aquaporin-4 (AQP4) antibody positive.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION UPLIZNA is contraindicated in patients with: A history of life-threatening infusion reaction to UPLIZNA…
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Infusion Reactions: UPLIZNA can cause infusion reactions…
INDICATION AND IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
INDICATION
UPLIZNA (inebilizumab-cdon) is indicated for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) in adult patients who are anti-aquaporin-4 (AQP4) antibody positive.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
UPLIZNA is contraindicated in patients with:
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Infusion Reactions: UPLIZNA can cause infusion reactions, which can include headache, nausea, somnolence, dyspnea, fever, myalgia, rash, or other symptoms. Infusion reactions were most common with the first infusion but were also observed during subsequent infusions. Administer pre-medication with a corticosteroid, an antihistamine, and an anti-pyretic.
Infections: The most common infections reported by UPLIZNA-treated patients in the randomized and open-label periods included urinary tract infection (20%), nasopharyngitis (13%), upper respiratory tract infection (8%), and influenza (7%). Delay UPLIZNA administration in patients with an active infection until the infection is resolved.
Increased immunosuppressive effects are possible if combining UPLIZNA with another immunosuppressive therapy.
The risk of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) reactivation has been observed with other B-cell-depleting antibodies. Perform HBV screening in all patients before initiation of treatment with UPLIZNA. Do not administer to patients with active hepatitis.
Although no confirmed cases of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML) were identified in UPLIZNA clinical trials, JC virus infection resulting in PML has been observed in patients treated with other B-cell-depleting antibodies and other therapies that affect immune competence. At the first sign or symptom suggestive of PML, withhold UPLIZNA and perform an appropriate diagnostic evaluation.
Patients should be evaluated for tuberculosis risk factors and tested for latent infection prior to initiating UPLIZNA.
Vaccination with live-attenuated or live vaccines is not recommended during treatment and after discontinuation, until B-cell repletion.
Reduction in Immunoglobulins: There may be a progressive and prolonged hypogammaglobulinemia or decline in the levels of total and individual immunoglobulins such as immunoglobulins G and M (IgG and IgM) with continued UPLIZNA treatment. Monitor the level of immunoglobulins at the beginning, during, and after discontinuation of treatment with UPLIZNA until B-cell repletion especially in patients with opportunistic or recurrent infections.
Fetal Risk: May cause fetal harm based on animal data. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use an effective method of contraception during treatment and for 6 months after stopping UPLIZNA.
Adverse Reactions: The most common adverse reactions (at least 10% of patients treated with UPLIZNA and greater than placebo) were urinary tract infection and arthralgia.
Please see Full Prescribing Information for more information.
INDICATION UPLIZNA (inebilizumab-cdon) is indicated for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) in adult patients who are anti-aquaporin-4 (AQP4) antibody positive.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION UPLIZNA is contraindicated in patients with: A history of life-threatening infusion reaction to UPLIZNA…
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Infusion Reactions: UPLIZNA can cause infusion reactions…
INDICATION AND IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
INDICATION
UPLIZNA (inebilizumab-cdon) is indicated for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) in adult patients who are anti-aquaporin-4 (AQP4) antibody positive.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
UPLIZNA is contraindicated in patients with:
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Infusion Reactions: UPLIZNA can cause infusion reactions, which can include headache, nausea, somnolence, dyspnea, fever, myalgia, rash, or other symptoms. Infusion reactions were most common with the first infusion but were also observed during subsequent infusions. Administer pre-medication with a corticosteroid, an antihistamine, and an anti-pyretic.
Infections: The most common infections reported by UPLIZNA-treated patients in the randomized and open-label periods included urinary tract infection (20%), nasopharyngitis (13%), upper respiratory tract infection (8%), and influenza (7%). Delay UPLIZNA administration in patients with an active infection until the infection is resolved.
Increased immunosuppressive effects are possible if combining UPLIZNA with another immunosuppressive therapy.
The risk of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) reactivation has been observed with other B-cell-depleting antibodies. Perform HBV screening in all patients before initiation of treatment with UPLIZNA. Do not administer to patients with active hepatitis.
Although no confirmed cases of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML) were identified in UPLIZNA clinical trials, JC virus infection resulting in PML has been observed in patients treated with other B-cell-depleting antibodies and other therapies that affect immune competence. At the first sign or symptom suggestive of PML, withhold UPLIZNA and perform an appropriate diagnostic evaluation.
Patients should be evaluated for tuberculosis risk factors and tested for latent infection prior to initiating UPLIZNA.
Vaccination with live-attenuated or live vaccines is not recommended during treatment and after discontinuation, until B-cell repletion.
Reduction in Immunoglobulins: There may be a progressive and prolonged hypogammaglobulinemia or decline in the levels of total and individual immunoglobulins such as immunoglobulins G and M (IgG and IgM) with continued UPLIZNA treatment. Monitor the level of immunoglobulins at the beginning, during, and after discontinuation of treatment with UPLIZNA until B-cell repletion especially in patients with opportunistic or recurrent infections.
Fetal Risk: May cause fetal harm based on animal data. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use an effective method of contraception during treatment and for 6 months after stopping UPLIZNA.
Adverse Reactions: The most common adverse reactions (at least 10% of patients treated with UPLIZNA and greater than placebo) were urinary tract infection and arthralgia.
Please see Full Prescribing Information for more information.